|
Data
Quality Assessment (DQA)
Data Quality Assessment (DQA) is a rigorous
scientific and statistical evaluation to determine if environmental
data are of the right type, quality, and quantity to support their
intended use. The process involves review of data quality objectives
(DQO), sampling purpose, sampling design, sampling methods,
documentation, analytical procedures, validation procedures, data
reduction procedures, review of database procedures, and review of
statistical methods used for decision making. The process is not
limited to analytical data, but includes all data types used by the
decision makers. Although data validation is often employed during
DQA, it is not always necessary. The question that needs to be
answered by the data quality assessment is "Are the data appropriate
for the intended use?
DQA is built on a fundamental premise: data
quality is meaningful only when it relates to the intended
use of the data. Data Quality does not exist in a vacuum, a
reviewer needs to know in what context a data set is to be used in
order to establish a relevant yardstick for judging whether or not
the data is acceptable. By using DQA, a reviewer can answer four
(4) important questions:
1-Can a decision (or estimate) be made with
the desired level of certainty, given the quality of the data?
2- How well did the sampling design perform?
3- If the same sampling design strategy is
used again for a similar study, would the data be expected to
support the same intended use with the desired level of certainty?
4- Is it likely that sufficient samples were
taken to enable the reviewer to see an effect if it was really
present?
It is important to note that the DQA process
covers all components of decision making including planning,
implementation, data review, and decision making. It is not a
process that is limited to review of analytical data
(see
data validation).
While data validation
and verification are
important processes,
they are activities that are often applied only to analytical data.
High quality analytical data can be useless if the samples were
collected improperly, if there are errors in the electronic
database, if improper statistical test were selected, or if the
sampling plan did not generate sufficient samples.
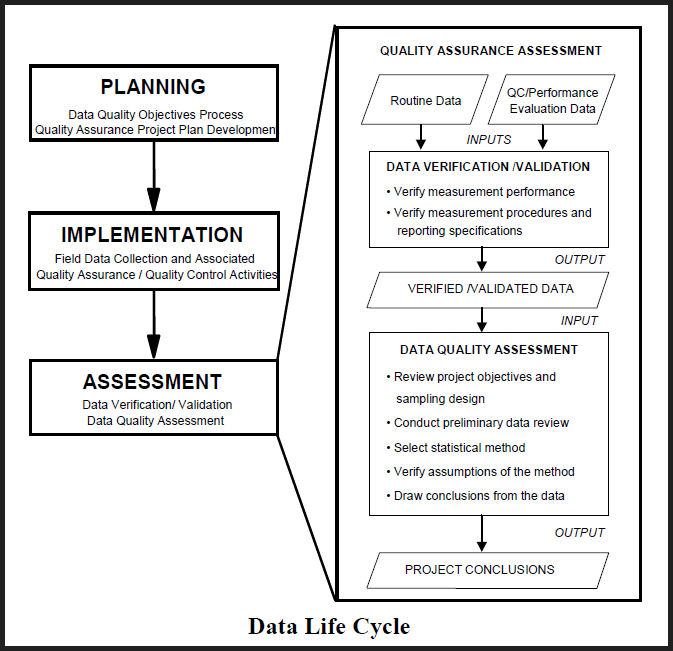
The five steps
in the DQA process are:
1- Review the
projectís objectives and Sampling Design
2- Conduct a Preliminary Data Review
3- Select the Statistical Test
4- Verify the Assumptions of the Statistical
Test
5- Draw Conclusions from the Data
We look forward
to the privilege of serving your project needs.
|